Explore how AI is being used to forecast delays, optimise schedules, and reduce risk in construction.
Construction is a complex, high-stakes game where delays are measured in thousands of pounds per day and surprises are rarely good news. For years, project managers have been asked to forecast the future using spreadsheets, Gantt charts, and experience. It’s worked - up to a point.
Now, AI is stepping in - not to replace the project manager, but to equip them with something they’ve never had before: real-time, predictive insight based on live data.
In the US, this shift is already well underway. AI-driven platforms like Briq.com are helping contractors plan better, react faster, and control risk with far more precision. In the UK, adoption has been slower. But the opportunity? It’s massive - and well within reach.

What Is Predictive Project Management?
At its core, predictive project management uses AI to analyse past and present project data to forecast likely future outcomes. That could mean:
- Predicting cost overruns weeks before they happen
- Identifying which subcontractor delays are most likely to escalate
- Highlighting task sequences that are creating critical path risk
- Flagging resource misallocations that lead to wasted costs.
Unlike traditional scheduling tools, AI-driven systems ask:
“Based on similar projects, current progress, and live data - how likely are delays?”
And when there are incoming delays, the system highlights why, when, and where problems will occur before they do.
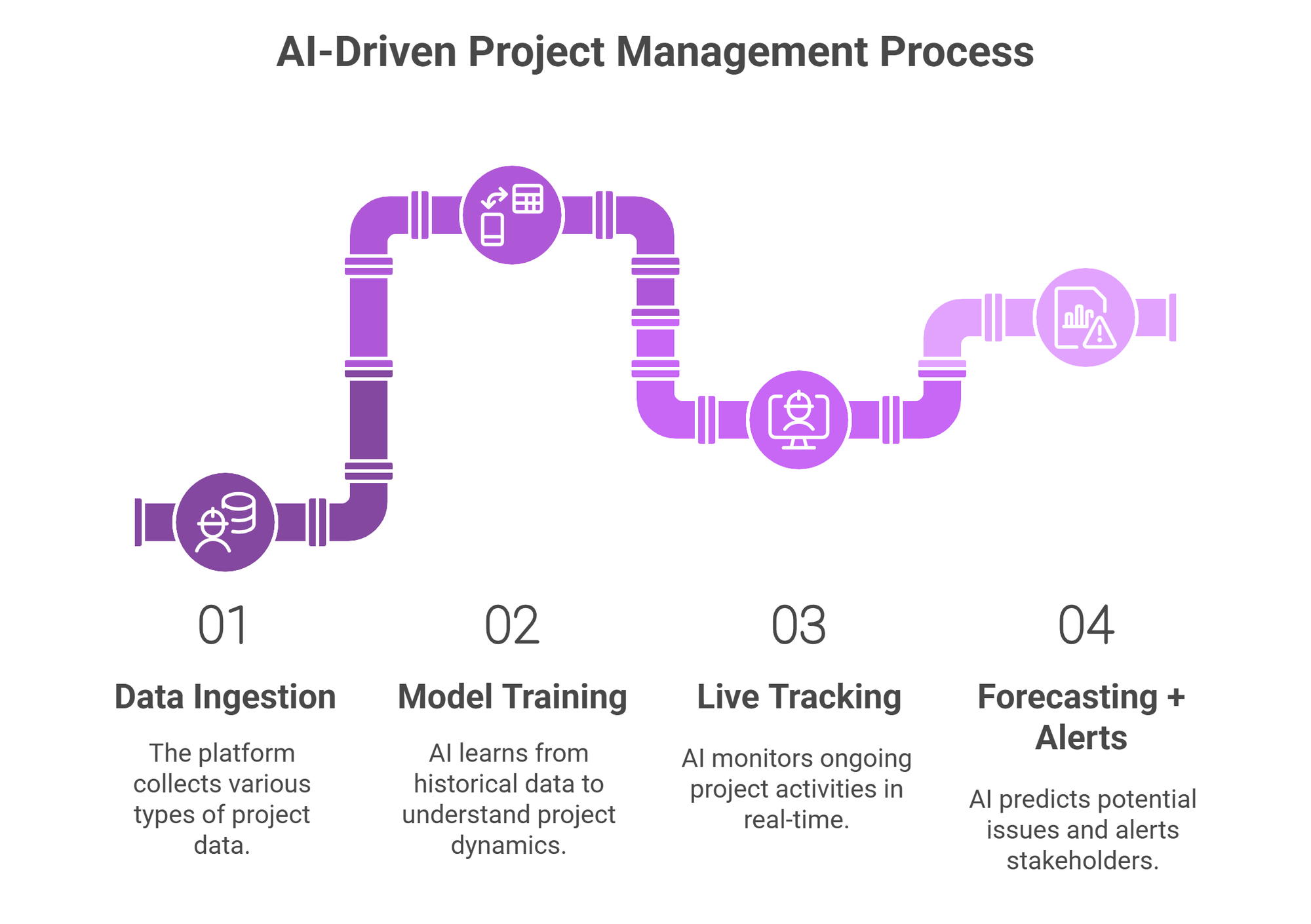
How the Technology Works (Without the Hype)
Let’s be clear: AI in this context isn’t “robotics” or “automation” in the sci-fi sense. It’s pattern recognition and forecasting at speed, and at scale.
Here’s how it works:
- Data ingestion: The platform takes in a wide range of structured and unstructured data:
- Schedules (Gantt charts, critical paths)
- RFIs, change orders, delay logs
- Resource data (labour, plant, materials)
- External data (weather, delivery timing, subcontractor information
- Model training: Using historical data, the AI “learns” what a typical successful (or problematic) project looks like. It builds a statistical understanding of what causes delays, costs, and inefficiency. How? Live tracking.
- Live tracking: As the project runs, the AI continuously monitors new inputs like subcontractor updates, delivery confirmations etc. Think of it as a permanently switched-on programme analyst, comparing what should happen to what is happening.
- Forecasting + alerts: When the AI detects signs of potential slippage, like a material delay that usually precedes structural work stoppage - it flags it. Not just that it’s late, but what the downstream effect will be, and what actions can mitigate the risk.
Example in Action
On a housing development, bricklayers are working through a row of houses, and roofers are due to start a week later.
The AI is reading - daily site diaries, subcontractor updates, and the programme.
It spots that brickwork is falling behind, not by a huge amount, but just half a day per plot. Most of the team hasn’t noticed, because it looks like steady progress. But the AI has seen this exact pattern on previous jobs - small delays that add up.
It predicts that if nothing changes, the roofers will turn up in 10 days - and only half the plots will be ready. That’ll cause a bottleneck, re-booking costs, and knock-on delays to windows and internal trades.
So it flags:
“Brickwork is slipping by 0.5 days per plot. If not corrected, roofers won’t be able to start on time. Recommend rebalancing labour or pushing back roofer start date by 3 days.”
The team checks it — and realises the AI’s right. They add one extra bricklayer and avoid the bottleneck completely. No dramas, no wasted time, no rebooking fees.
AI for Scheduling & Resource Allocation
Beyond forecasting, AI is now being used to actively optimise construction programmes to speed up delivery.
Key capabilities include:
- Sequence optimisation: AI analyses millions of possible task sequences to find the most efficient construction path - factoring in constraints like weather, labour availability, delivery windows, and site logistics.
- Dynamic rescheduling: When an event (e.g. crane breakdown, delivery delay) occurs, the AI recalculates the best path forward - redistributing crews, adjusting timelines, and flagging knock-on effects.
- Resource allocation: AI identifies gaps in labour use and recommends reassignments that reduce idle time and cost. For example, moving a crew from one task to another before they hit downtime.
Think of it like a real-time construction strategist - always watching the moving parts, and suggesting the most efficient course in terms of time and cost.

Briq: A Real-World Example
Briq, a US-based platform, is a leader in this space. It’s focused on the financial side of predictive project management, connecting cost forecasting with schedule analysis.
What it does:
- Integrates project budgets, schedules, and actual spend
- Uses AI to forecast cash flow, margin erosion, and schedule slippage
- Sends early alerts when project performance trends deviate from expected baselines
Why it matters:
- Instead of waiting for a month-end review to find out a job is off-track, PMs can see it live
- Project teams can adjust before the damage is done
- Executives get portfolio-level views of risk across multiple projects
In practice, this means fewer surprises, faster reporting, and more proactive decision-making.
What UK Firms Can Do Now
You don’t need to overhaul your entire tech stack to get started.
Here’s how to take practical steps into AI-driven project management:
- Audit your data: Clean data is essential. Start collecting and organising delay logs, resource usage, weather impacts, and programme performance. Even simple Excel-based tracking is useful.
- Run a pilot: Apply AI forecasting on a mid-risk job. Use the outputs to challenge assumptions and stress test schedules—not to replace them.
- Train your team to ask better questions: You don’t need data scientists - but you do need planners and PMs who know how to interpret AI forecasts and act on them.
Conclusion: Construction’s Crystal Ball Has Arrived
AI in construction isn’t hype anymore. It’s a set of tools that can make projects run smarter, forecasting trouble before it hits, optimising schedules in real-time, and making sure that boots on the ground aren’t left waiting for materials that haven’t arrived.
The US is already proving this at scale. But the UK has the talent, the projects, and the digital runway to follow fast.
If construction is all about risk, time, and margin, then AI’s role is clear:
Better project insights. Better outcomes.





